What can we do to keep the fire in our children’s eyes burning brightly? How can families and teachers give children the life skills they need to cope in our multi-tasking, multimedia, modern world? These are the central questions Ellen Galinsky explores in the book, Mind In The Making: Seven Essential Life Skills Every Child Needs.

I had read Mind In The Making shortly after it was published in 2010, and was avidly following Amanda Morgan’s (Not Just Cute) series of “read along” posts delving deeply into the contents of the book, so I was thrilled to have the opportunity to meet Ellen during a recent talk she gave about the book. Ellen introduced Mind In The Making as an “accidental book”- one that took over ten years to write. She explained, “I didn’t set out to write a book. I started with the idea of doing a study on Youth and Learning. But- “In the course of interviewing young people (from many different backgrounds) for the study, I found far too many of them were turned off by learning, which is in stark contrast to very young children, who are driven to learn. I postponed the study on Youth & Learning and began a journey to answer the following questions: 1) How do children learn best? 2) What makes them stay motivated and engaged in learning? 3) What makes them see themselves as learners, and how do they become ongoing, life-long learners? 4) What can be done to rekindle their motivation if it has been dulled?”
Ellen then decided to make a documentary exploring the best science on children’s learning. But, after a few months of interviewing researchers and working with a production company to film experiments, the documentary grew to become a series. Four to five years later, after examining research across many disciplines, Ellen said she began to see a certain set of skills that emerge in all children who are motivated, engaged learners. She could also see, from looking at longitudinal research, that if parents and teachers promoted these skills, it made a critical difference, and helped children to thrive throughout their lives, which is why she defined the seven skills she identified as life skills. She quipped, “Everyone does something. Some people kayak, and others climb mountains for adventure. I follow research and call it adventure.” My kind of lady!

All seven of the skills Ellen identified involve what scientists call executive functions of the brain. (Executive functions all involve the prefrontal cortex of the brain, and we use them to manage our attention, our emotions, and our behavior in order to reach our goals. They aren’t just intellectual skills (what we typically think of as IQ), but also encompass social and emotional capacities, and “go beyond what we know, to tap into how we use what we know.” The seven life skills are as follows:
- Focus and Self Control
- Perspective Taking
- Communicating
- Making Connections
- Critical Thinking
- Taking On Challenges
- Self Directed, Engaged Learning
Ellen went on to explain that she wanted to write a book that would bring the research alive in an interesting and engaging way, and not guilt parents, but instead, be hopeful and help them to see how they could nurture their children’s development of these seven life skills through everyday interactions and activities. I’d say she succeeded brilliantly in her goal.
She stressed that these skills are as important for adults as they are for children, and that when we practice them ourselves (modeling), we help promote them in children. “We don’t need expensive programs, materials, or equipment to promote these skills- they can be promoted through the everyday things we do with children, and it’s never too late to help children learn these skills- no matter what their age.” During her talk she used video clips to introduce various researchers and bring the research alive, by bringing us into the lab to watch experiments in action, and in the book, she shares numerous examples that translate the research into “real life” situations. She provides a parent’s perspective, and shares some of her own experiences and lessons she learned from parenting her two (now grown) children. She also offers short experiential exercises for adults, and many suggestions for enjoyable and easy ways for parents and teachers to encourage and support children in developing the seven life skills- through the conversations we have, the games we play, the routines and rituals we develop, and even through the difficulties and disagreements that naturally occur between siblings or between parents and children. (Sibling relationships provide fertile ground for helping children to develop their skills in perspective taking or “understanding the other”, communication, and problem solving!)
There was a group of early childhood educators seated behind me in the auditorium, and I had to grin when one of them couldn’t contain an enthusiastic, “Uh huh! What took them so long to figure that out?”, as Ellen underscored the point that young children learn and solidify focus and self control through active movement of their bodies. What is often very obvious and “known” to those of us who care for, teach, and observe young children on a daily basis is just now being studied, understood, and quantified by researchers.
What was exciting to me as I was reading the book and listening to Ellen speak, is what the researchers are now discovering about babies and toddlers and how they learn. Most people don’t think to pair the word “competent” with infants, yet, they are competent to begin participating in relationship and learning from their first moments, and the research provides some striking examples of ways we can support even the youngest and most fragile of babies to begin to develop the skills they will need and use for life. I am especially interested in making connections between the current research and my practice of Magda Gerber’s philosophy of educaring (educaring = teaching while caring).
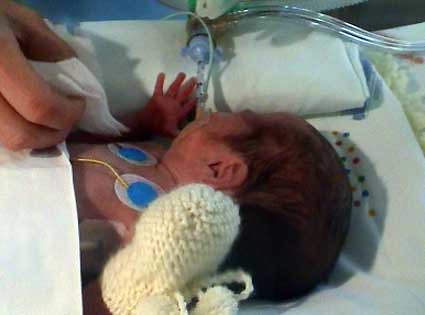
Particularly fascinating to me, and what I want to highlight in this post and the next, is Heidelise Als’s (of Harvard University) research with preterm infants (born ten to twelve weeks before their due date) in neonatal intensive care units. Als’s work points to the tremendous competence and resilience even the most fragile baby is born with. Ellen shares in her book that her son Philip was born premature, so Als’s research was of particular interest to her, as well. Ellen believes Als’s work has important implications for all children, because it is instructive in how we can work with children to help them to thrive and cope in the face of challenges, becoming stronger in the process.
This short video clip provides a brief interview with Als, highlights how her ideas are benefiting some premature infants, and suggests why her findings might be helpful to all of us interested in helping children to develop their inborn abilities to take on challenges and cope with stress. I invite you to take a moment to watch.
In my next post, I will share more about Als’s discoveries and approach, which she describes as a developmental, relationship based, respectful way to support even the youngest infants to manage their own stress, by encouraging them “to use the abilities that they are born with for coping and calming down.”
I’ll leave you with this quote from Als, which is where I begin my next post….
“If we can understand the ‘words’ the baby is saying, maybe we can fill in the meaning of the sentence and understand the message.”
