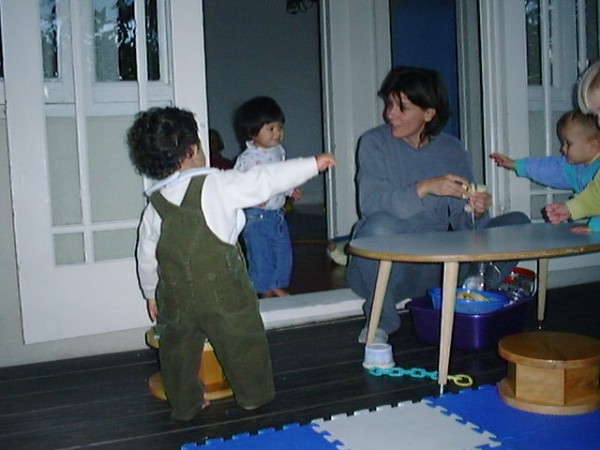
“Help! My toddler has discovered climbing and tries to climb everything — chairs, tables, gates, bookcases. I am constantly telling him no and pulling him down from things. When we’re at someone else’s house it’s hard to enjoy myself because I’m always chasing him. What can I do to get him to stop? Or is climbing a good thing?” When and where is it appropriate to allow babies and toddlers to climb? Should they be allowed to climb on furniture or in the shopping cart areas of store parking lots because they want to and they are capable of doing so?
Many children go through a stage of wanting to climb on everything, and some never seem to outgrow the desire to climb! Children develop their self confidence, balance, judgement, planning skills, eye/hand coordination, perseverance, and more as they climb and move their bodies through space, so why not let them climb anywhere and everywhere they choose to? You might be surprised to hear that I discourage allowing young children to climb on furniture, (or in public places like store parking lots that aren’t designed for this purpose), and my reason for doing so doesn’t have as much to do with safety concerns (although safety is a consideration), as it does with the fact that furniture is not made for climbing on, and while I encourage and support children to move, explore, and play freely, I also feel strongly about guiding young children to learn to respect not only themselves, but other people, and their environment. The reality is that we live in relationship and community with others, and children first learn about expectations, boundaries, and social mores at home with parents and siblings. I think babies and toddlers are able to understand that there are places and times appropriate for climbing, and others that aren’t, and a child’s desire (and maybe even need) to climb and explore can be met even as loving adults guide him to appropriate places to practice and hone his physical skills.
I once worked in a childcare center as a member of a teaching team of three, caring for a group of seven infants and toddlers ranging in age from three to fifteen months. A frequent topic of conversation during our weekly planning meetings was how to utilize our classroom space to best meet the developmental needs of the group. We were lucky to have access to a number of movable pieces of wooden climbing equipment, and a twin sized mattress, so the possibilities for creative and challenging room arrangements were many. We also had access to a fenced, grassy, shaded play yard with climbing equipment suitable for mobile babies and young toddlers.
We had a wide open floor plan, with floor to ceiling windows against one wall, a separate nap room, a designated area for diaper changing and a small kitchen area with a linoleum floor and a toddler sized table and chairs. There was a rocking chair for adults to sit in while feeding babies a bottle. One of the most frustrating aspects (for children and adults) of this floor plan was that while we endeavored to create an environment that allowed the children to play and explore freely, we often found ourselves having to stop inquisitive and eager new explorers from climbing over the non-mobile babies, or on the table or the rocking chair, or from trying to scale the low wooden toy shelves. The children often made no distinction between the “approved” climbing equipment, and the other babies or the utilitarian pieces of furniture in the room, and in fact, sometimes seemed to prefer the furniture for climbing.
My colleagues argued that we should patiently and consistently let children know that other children, the table, chairs, and the rocking chair weren’t for climbing, which meant stopping them and showing them where they could climb instead. If a child was particularly persistent, and not easily redirected we resorted to “containing” him for a short while by sitting him in a chair at the table with a book or a few toys, or maybe by taking him and a few friends for a walk outside in the stroller. In theory, this sounded like a good idea, but in practice, we ended up spending a lot of our day redirecting babies and saying no, which was frustrating for them and for us, especially since there was usually only two adults in the room at a time, and one of us would inevitably be busy changing, feeding, or helping a baby in the nap room, while the other supervised the remaining children.

I had a nagging discomfort, a feeling that somehow we weren’t meeting the needs of the children very well, because (my rationale went) if they were so driven to climb, we either needed to provide an environment that met and allowed for that need without us having to constantly redirect them, or maybe we should let them climb wherever they wanted to, and not restrict them (except for when it came to climbing over other babies). After all, with the exception of the glider, which could potentially tip over if a toddler stood up on it, none of the furniture posed a very big safety risk. My colleagues maintained that it was important for the babies to learn that some places were for climbing, and others weren’t. I didn’t know if I agreed if it meant spending my day “putting out fires” and redirecting babies to other areas of the room, or somehow confining them.
In the midst of my search for answers to this dilemma, I was introduced to Magda Gerber’s idea of creating a totally safe, but challenging, play environment for babies in which they are free to explore and move as they wish without a lot of interference or direction from adults. This seemed like an impossible task to accomplish given our floor plan and the fact that we were caring for seven babies of varying ages and developmental abilities in the same room. Much to my surprise, there was a simple answer to our dilemma, and that was to use sturdy gates to create very clear environmental boundaries for babies. The other solution was to stop rearranging and re-configuring the room on a weekly basis as we had been doing- the theory being that the babies didn’t need novelty as much as they needed consistency and predictability.
We decided to try this idea, using gates to partition the room into four distinct areas- one for feeding, another for diaper changing, a small play area for non-mobile infants, with the largest part of the room becoming a play and climbing area for mobile babies and toddlers, with a cozy quiet nook under the climbing structure. The “creation” of distinct areas for certain tasks immediately reduced the need for adult intervention and redirection by about 90%. It was clear to the children what the purpose of each area was, and despite the gates, which had to be opened and closed by the adults, the children actually had more freedom and choice than they had enjoyed previously.
This was the beginning of my understanding of how to “use” or adapt the home or school environment to create safety and freedom within clearly defined limits. So, how might this lesson translate in a home and family environment if you’ve got a little climber on your hands, and you want to encourage and support her growing physical prowess and mastery? What can you do to allow her to exercise her desire to test her limits, while also helping her to learn to exercise some self control, learn social graces, and to utilize furniture for its intended purpose as opposed to using furniture as her personal climbing gym? Here are some ideas:
Two Ideas For Creating Inexpensive Outdoor Climbing Opportunities In A Small Space
- 1) Childproof and use gates in your home and yard to block off areas or rooms that are off limits unless you are able to be present and available to intervene and model desired and expected behavior. If you are able to, consider dedicating a room or part of a room to creating a completely safe play area, and start spending time with your baby in this play space from day one.This space can evolve as your child grows and her needs change. If you’ve got stairs in your home, use them to allow your child to practice climbing. Do this by using a sturdy gate to block off all but one or two stairs, and then gradually increase the number of stairs she has access to as she becomes more confident.
2) Within the environment you have created, allow your child free, unrestricted movement. Stay nearby to observe, but don’t put babies into positions (or lift them onto equipment) they can’t get into by themselves. In this way, they will develop good judgment about what they can and can’t safely do. Surprisingly, a recent news article pointed to the fact that a common playground injury (a tibia fracture) often occurs when parents slide down playground slides with their toddlers on their laps! Magda Gerber urged parents to allow babies to move in their own time and their own way, according to their inner dictates,”Whenever you restrict an infant from doing what he could and would do naturally, in my mind you tell the child, “I know what’s good for you.” But you, the adult, do not know. For example, most children (not all), when they first go down stairs, go head first-they like to see where they go. Some people say it’s safer for infants to crawl down stairs backwards, and they teach infants how to go down that way. The child may become confused because his body tells him one thing and the adult another, and then the child may fall.”
3) Consider adding a few simple pieces of play equipment to your indoor space that are appropriate for, and invite climbing. This can be especially important and helpful if you live in a small home and don’t have easy access to a yard, or if you live in climates that make outdoor play prohibitive at times. Here are some suggestions for climbing equipment that is sturdy but easy to move, and can be used indoors or out: I recommend the Step 2 Naturally Playful Lookout Treehouse and Community Playthings Step Climber/Rocking Boat. (You can often find perfectly good, used equipment at garage sales for a fraction of the price of new.) Here is a link to a site that sells child size table and chairs, and climbing equipment like the kind we utilize in RIE parent/infant classes.
4) Spend lots of time outdoors, at playgrounds or parks. Let your children climb rocks, trees, slides, monkey bars, and hills to their heart’s content. If the weather prohibits this, consider finding and using an indoor children’s gym or play area that has free play time. (I’d recommend avoiding organized movement classes or directed play until children are well past the preschool age.)
5) Remain calm and consistent when setting limits with your young toddler around climbing. “You want to climb on the table, but I don’t want you to climb here. The table is where we sit to eat. If you want to climb, you may climb here (showing him).”
What do you think? Do you allow your child to climb on furniture at home? Why or why not? If not, what have you found works to help satisfy your child’s desire to explore his desire to climb?